- DNA Replication -
DNA replication: cell division occurs in 2 main stages:
Semi-conservative replication ~ this ensures the genetic continuity between generations.
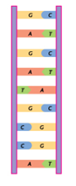 The enzyme DNA helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds between complementary bases in polynucleotides strands, causing the double helix to unwind/unravel.
The enzyme DNA helicase breaks the hydrogen bonds between complementary bases in polynucleotides strands, causing the double helix to unwind/unravel.
 .
.
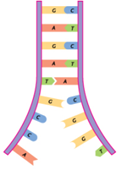
 The enzyme DNA polymerase joins adjacent nucleotide's in a condensation reaction.
The enzyme DNA polymerase joins adjacent nucleotide's in a condensation reaction.
The exposed nucleotide's act as a template to which the complementary free nucleotide's bid by specific base pairing
 2 identical molecules of DNA are formed. This is due to each molecule retaining half of the original DNA material. Watson and Crick model of DNA replication suggested that the original DNA molecule splits into 2 separate strands therefore each of the new molecules would have one strand of the original material. This would be the semi-conservative model. The conservative model suggests that the original molecule remained intact and the other molecule formed would be made of entirely new material.
2 identical molecules of DNA are formed. This is due to each molecule retaining half of the original DNA material. Watson and Crick model of DNA replication suggested that the original DNA molecule splits into 2 separate strands therefore each of the new molecules would have one strand of the original material. This would be the semi-conservative model. The conservative model suggests that the original molecule remained intact and the other molecule formed would be made of entirely new material.

No comments:
Post a Comment