- Principles Of Homeostasis -
What is Homeostasis?
This is the maintenance of an interval environment within restricted limits in organisms.
This is to ensure that the chemical make-up, volume and other features of blood and tissue fluid within restricted limits are maintained.
Homeostasis is the maintenance of a stable internal environment.
Any changes that are made to the external environment can affect the internal environment of an organism.
To prevent this, homeostasis is involved in control systems that would maintain the constant internal environment.
To prevent this, homeostasis is involved in control systems that would maintain the constant internal environment.
This allows virtual cells to function normally and prevent damage to them and they are kept in a stable environment.
Factors that would be maintained ⇒ the core body temperature and blood pH.
This is because both pH and temperature are factors that effect enzyme activity and enzymes control the rate of metabolic reactions.
Temperature: if it is too high or at an extreme the enzymes would become denatured.
This is due to the hydrogen bonds breaking that holds them in their 3D shape. Thus changing the active site, which leads to an ineffective catalyst.
This is due to the hydrogen bonds breaking that holds them in their 3D shape. Thus changing the active site, which leads to an ineffective catalyst.
If the temperature is too low the enzyme activity is reduced and it slows down the rate of metabolic reactions.
In order for the rate of enzyme activity to remain at a constant the enzymes have an optimum temperature at which they work best at. In humans, this would be 37oC.
pH: if the pH is too high or too low // at either ends of extremes// the enzymes denature. Hydrogen bonds that hold the shape of the enzymes are broken. Therefore, the active site of the enzyme is changed which makes it ineffective catalyst. The metabolic reactions are less efficient.
The highest rate of enzyme activity remains at an optimum pH // usually remains around pH 7.
But this varies for some enzymes // enzymes for the stomach work best at a low pH.
Because cells need glucose for energy it is important to maintain the right concentration of glucose in the blood.
Blood glucose concentration also affects the water potential of blood - there is the potential that water molecules diffuse in and out of or into a solution.
If blood glucose concentration is high ⇒ water potential of blood is reduced // water molecules would then diffuse out of the cell // osmosis // cell will shrivel up and die.
If blood glucose concentration is too low ⇒ cells cannot carry out normal activities there isn't enough glucose for respiration to provide energy.
- The control mechanisms -
Control of any self regulating system involves a series of stages
- Optimum point
- Receptor
- Coordination
- Effector
- Feedback mechanism
- Receptor
- Coordination
- Effector
- Feedback mechanism
Homeostatic systems detect change and respond by negative feedback.
1) The receptor, communication system and effectors is the foundation of the homeostatic system.
2) Receptors are there to detect when there is a change in temperature - this would be when temperature is too high or too low. Via the nervous system or hormonal system the information is passed on to the effector.
3) The effectors are suppose to counteract the change // bring the level back to an optimum.
4) Negative feedback = process of bring the level to an optimum temperature.
5) Negative feedback keeps the body's temperature at an optimum which is above 0.5℃ or below 37℃.
6) However if they change is too drastic then the Negative feedback would be unable to counteract the change. This can be when there has been prolonged exposure to cold weather.
There are multiple Negative feedback mechanisms ⇒ more control. By only having one negative feedback system ⇒ there is a slower response and less control.
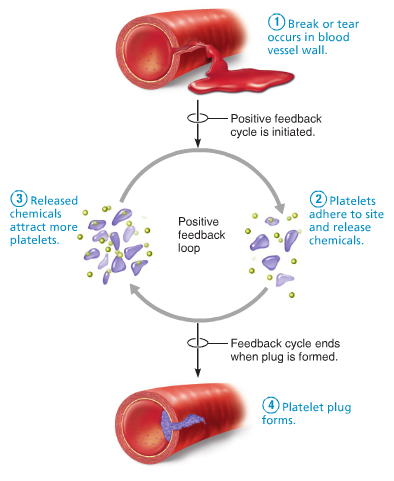
Positive feedback mechanisms can amplify a change from the normal level.
1) some changes can trigger a positive feedback // amplifying the change.
2) Increasing the level further away from the normal level.
3) Positive feedback rapidly activates something // Blood clot after a deep cut.
4) Positive feedback can occur when homeostatic system breaks down e.g. Being too cold for too long.
Positive feedback is not involved in homeostasis because it does not keep the internal environment stable.
Control system normally have receptors and effectors allows them to have separate mechanisms that produce a positive movement towards an optimum. Allows greater degree of control of the particular factor being regulated.
Positive feedback is not involved in homeostasis because it does not keep the internal environment stable.
- Coordination of control mechanisms -
Control system normally have receptors and effectors allows them to have separate mechanisms that produce a positive movement towards an optimum. Allows greater degree of control of the particular factor being regulated.
No comments:
Post a Comment